

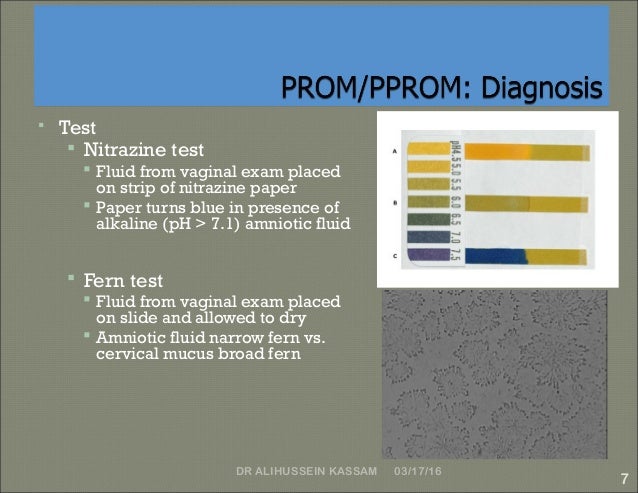
Negative Result : No fetal membrane rupture Positive Result : Fetal membrane rupture is detected ONE TEST - In trials, AmniSure ® correlated with the clinical diagnosis obtained through the combined usage of three routinely used tests (Nitrazine, Ferning, and Pooling).MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES - New generation device employing immunochromatographic method.ONE SHORT INCUBATION - Produces quick results - within minutes.SIMPLE PROCEDURE - No need for speculum examination, additional reagents or equipment and the result can be evaluated visually.Diagnosis of ruptured fetal membranes is of crucial importance at any term in a pregnancy for prompt hospitalization and for timely and proper treatment. If the rupture of the amniotic sac that results in the leakage of the fluid is not detected and treated in a timely and accurate manner (within 24 hours from the occurrence of the rupture), infection and other serious complications for the neonate and the mother may occur. In the U.S., at least 30% of pregnant women are checked for PROM during pregnancy
Premature ROM (PROM) occurs in about one out of ten pregnant women and constitutes the major factor of pre-and post-natal complications. that solves a long-standing problem in obstetric practice - diagnosis of ruptured fetal membranes (ROM). Their next phase of research will focus on detecting various cancer and heart disease biomarkers.AmniSure ® is a new diagnostic device developed by N-Dia, Inc. The researchers used similar technology to detect proteins in SARS-CoV2, the virus that causes COVID-19. The researchers were able to detect beta-2-transferrin in the fluid sample even when other proteins and salts were present and from samples across different patients. The circuit board then analyzed the signal and produced a four-digit number that correlates to the concentration of the protein, called beta-2-transferrin, found in CSF. Once the test fluid was inserted into the liquid channel, a few short electrode pulses were sent through the electrodes. The liquid channel held electrodes, which contained antibodies on the surface specific to proteins found only in human cerebrospinal fluid. The researchers collected nine human clinical samples from a Florida hospital and introduced the test fluid into a small liquid channel on the tip of the sensor strips. "We were surprised to find out that our detection method could not only provide the result within one second, but our detection limit was also a lot more sensitive for a very diluted concentration than existing detection methods," said co-author Minghan Xian. Cerebrospinal leaks can come out through the nose or the ears.

In addition to trauma, surgery and congenital defects, CSF leaks are likely to occur because of obesity, high intercranial pressure, and obstructive sleep apnea. CSF directly links extracranial space to subarachnoid space, a compartment within which are the major cerebral blood vessels. In Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology B by AIP Publishing, researchers from the University of Florida and Yang Ming-Chiao Tung University developed a single-use sensor strip that can be used with a circuit board, like a hand-held glucometer, to detect cerebrospinal fluid leaks.Ĭerebrospinal fluid is present in the brain and spinal cord and provides critical physiological functions, such as shock absorption and waste removal. Secondary methods, such as optical techniques that rely on MRI, often fail to identify the specific leak site. Detecting such leaks using primary conventional methods, such as immunofixation electrophoresis (IFE) and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), require hours or days to turn around results.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
